Dark Matter Can Illuminate Black Hole Shadows
A new study published in Physical Review Letters, with Yifan Chen among the authors, was selected as an Editors' Suggestion. It demonstrates that black hole images from the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) can serve as powerful probes of dark matter.
Unveiling the microscopic nature of dark matter is one of the biggest challenges in modern physics. One important approach is indirect detection, which searches for astrophysical signals from dark matter annihilation or decay into Standard Model particles such as photons or neutrinos. Near supermassive black holes, extreme gravity can concentrate dark matter into dense "spikes," with energy densities orders of magnitude higher than those in the solar neighborhood. This greatly enhances annihilation rates, making these regions uniquely promising for observation.
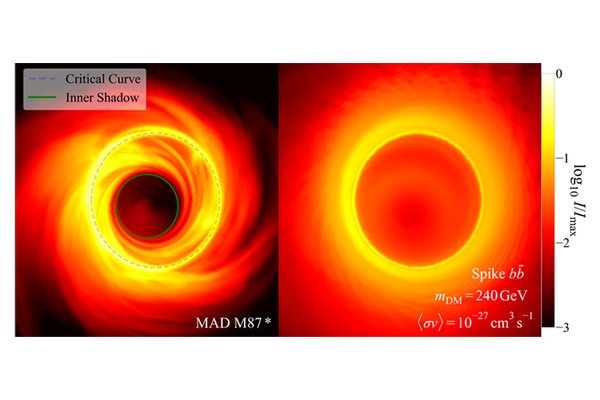
The EHT's images of the supermassive black hole M87* reveal a dark "shadow" encircled by a bright photon ring. The study shows that the faintest region of this shadow, the "inner shadow," shaped by light bending near the horizon, is especially sensitive to radiation from dark matter annihilation. Unlike ordinary plasma, typically expelled by jets, dark matter annihilation continuously injects electron-positron pairs, which radiate synchrotron light and illuminate this otherwise dark zone, as shown in the right panel of the figure above.
To ensure robust constraints, this study developed the most advanced framework to date for modeling electron–positron propagation in the strong gravity and magnetic fields near black holes, grounded in general relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations calibrated to current EHT data. The results rule out wide ranges of previously unexplored dark matter models and establish black hole imaging as a new frontier for fundamental physics. Looking ahead, upgrades to the EHT, particularly improvements in dynamic range, will sharpen sensitivity by probing even darker shadow regions.
Publication:
Yifan Chen, Ran Ding, Yuxin Liu, Yosuke Mizuno, Jing Shu, Haiyue Yu, Yanjie Zeng. "Illuminating Black Hole Shadow with Dark Matter Annihilation", Physical Review Letters, 135, 121001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/yxqg-363n
Sept. 22, 2025, 8:19 a.m.